Compared to USB-A, not really that much of a game changer (it’s still the most common for me). Though I do not miss the three rotations to get it in.
Compared to Micro-USB? Holy fuck, I almost refuse to buy anything still using Micro-USB ported now. Mainly because I can’t never find the fucking cable for it.
Though I do not miss the three rotations to get it in.
The holes point up or to the right.
Fucking awesome, it is. When I travel, I take 1 laptop power cord. Charges my phone, laptop, Switch, and backup battery. (The backup battery’s output ports are USB-A, but it’s got a lil converter cable that stays in the lil bag that the backup battery is stored in.)
So far it’s a mess.
I still have Micro USB devices, so I need two cables or USB-C→Micro USB adapter.
I have PCs without USB-C ports, so another adapter needed USB-C → USB-A.
But, I can now “dock” my new-ish laptop with only one USB-C ↔ USB-C cable to a monitor.
Monitor gives power.If your PC has PCIE slots you can get a USB-C card for around $25
Make sense, thanks.
I’m still in the messy stage, but I’ve made preparations for C. Pretty soon I’ll get a newer used phone and tablet, and they’re both going to be type C.
Currently I have a few things that use C, so I’ve already got some cables and chargers for them. Once the transition is complete, I’ll get rid of a bunch of old cables.
Usbc-pd is an absolute game changer as an off grid person. The fact a 100w charger can act as a dc to dc converter with up to five output voltages, at up to 100 watts is crazy. And that the protocol automatically detects and communicates the proper voltage is very convinent. The problem is that usbc-pd 100w chargers are expensive and you need to know what you are doing if you want to diy power appliances with it.
Its really nice to have a standardized cable that just works and can be plugged in both ways. We really are approaching a Universaal Cable after a quarter century of RnD.
I’m curious as to what exactly you do with it as an off-grid person, and what you mean by DC-to-DC converter.
Im happy to explain pastermil. So first off let’s talk power.
Electrical Power Systems
Most off-grid electrical systems have a few major components.
-
A device that generates electrical energy
-
A battery that stores excess electrical energy for later
-
A charge controller which regulates the incoming raw electrical power from the generator as it charges up the battery, and smooths out the battery energy output
-
A power distribution interface which allows for connecting appliances to the batteries in a safe standardized way.
My particular electric system has a 200w 28v solar panel for power generation, two 20ah lifepo4 batteries connected to double capacitance, and the charge controller doubles as a very basic interface with two usba slots and a car cigarette port.
AC vs DC
Now let’s talk about AC and DC. Theres essentially two kinds of electrical power people deal with.
The difference between Alternating Current and Direct Current is in the way the power flows. Direct current moves in a straight path. Alternating current moves power back and forth in three perfectly spaced cycles.
AC The one most people are more familiar with is AC power. it comes to your home from power plants through power lines and transformer boxes. You move around extension cords and plug the three prong outlets into a wall.
Alternating Current (three phase) power is very easy to transmit long distance however its very high voltage. So only certain power hungry devices like kitchen appliances, washing machines, dryers and AC compressors use it directly. Most of your consumer home devices need to convert AV power down into more manageable DC power.
DC Offgrid electrical systems with batteries are Direct Current by nature. All your power comes from the battery banks. The power moves straight from battery terminal negative to positive. It flows right through your appliances in one way out the other.
The battery banks tend to be arranged into 12v, 24v, or 48v depending on the systems power draw and transmission needs.
The popular standards for delivering direct current are:
-
5v 2.4a usb (15 watts)
-
12v 10a car cigarette plugs (120 watts, can be rated to supply 24v fused 15a I believe though not common at all)
-
circular dc barrel plug connectors, the most common size is 5.5mmx2.5mm but there are dozens if not hundreds of slightly different barrel plugs. Part of what makes usb so great is reducing arbitrary manufacturing complexity like this.
-
usbc-pd various voltages depending on charger, cable, and device at up to 100w for current protocol.
-
solar quick connects tend to be for connecting and transmitting high voltage DC power to charge controllers and power banks. Its worth mentioning but not that relevant to what were talking about.
Most consumer devices in your home dont actually use wall outlet AC power directly, it uses wall power thats been converted and stepped down to DC power.
Desktop computer power supplies, Laptops, monitors, vaporizers, led lights, DVD players, audio speakers, your phone. everything that can powered by usb and batteries. Everything that has barrel plug inputs and power bricks plugging into it.
If you look closely on the power bricks plugged into the appliance you’ll see that it has an input and output voltage rating. The input tends to be 120vac here in america 240v over the pond, and the output tends to be either 5v, 9v, 12v, 15v or 20v DC usually up to 5 amps.
Device vs Voltage Examples
Laptops and computer monitors tend to be 20v, fast charging smart phones and the Nintendo switch docked are 15v, very bright home LED lights can be bought that are powered at 12v directly, the ps2 could be powered with 9v, and most usb devices charge at standard 5v. Would you like to guess which voltage profiles the USBC-PD protocol is capable of? Its all of them.
Energy Conversion Efficency Losses
Now let’s discuss energy efficiency. Converting from AC to DC eats up some of your power. So does converting from DC to AC. And its not small losses either, each time you convert its about a 15% total loss in efficency.
This loss through conversion doesn’t matter when you pay cents on a kilowatt and have unlimited power at the tap. It adds up very quickly when you have a limited power supply and every watt hour counts.
Let’s say I want to power a laptop on my offgrid DC system and my only means of powering it is the AC power brick cable that it came with. I would need to:
- Convert the DC power of the batteries to AC through an inverter. 15% efficency loss.
- Then convert that power right back down into slightly different DC with the power brick plugged in. 15%% efficency loss.
- The inverter and power brick are both parasitic draws. They eat a bit of power just sitting there even if nothing is being powered. Lets add 5% total system efficency loss each.
Add these up and you get 30-40% of your power eaten away by this needless double converting. Wouldnt it be really nice if we could convert the battery DC voltage directly to the appliance DC voltage without those power hungry inverters and transformers?
What DC-to-DC Converters Are
Thats where dc to dc converters come in. They can convert one DC voltage to another. They still introduce efficency loss but way way less only 10% total.
Traditionally you would hope your device had a commercially available 3rd party travel adapter for 12v car batteries. The dc to dc converter is built in and uses car plug.
If you were SOL you has to wire up boost converters to raise up voltage and add resistors in series to lower it. You ever try to wire and solder your own circuts before? Its a tedious experience. Imagine doing that for each device voltage. Oh wait, you dont have to. Here’s what that looks like.
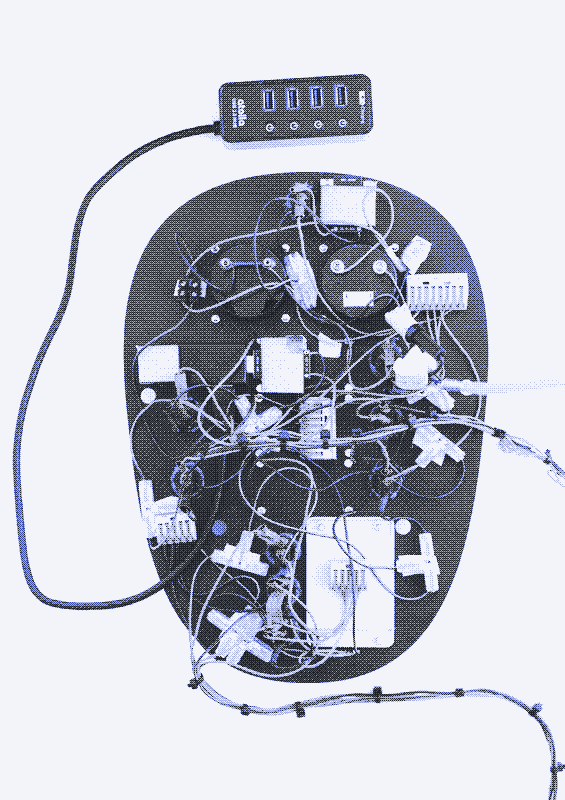

A USBC-pd 100w charger that plugs into a cigarette port or is built into a power bank can convert a batteries 12vDC into 5v, 9v, 12v 15v, and 20v dynamically depending on the device.
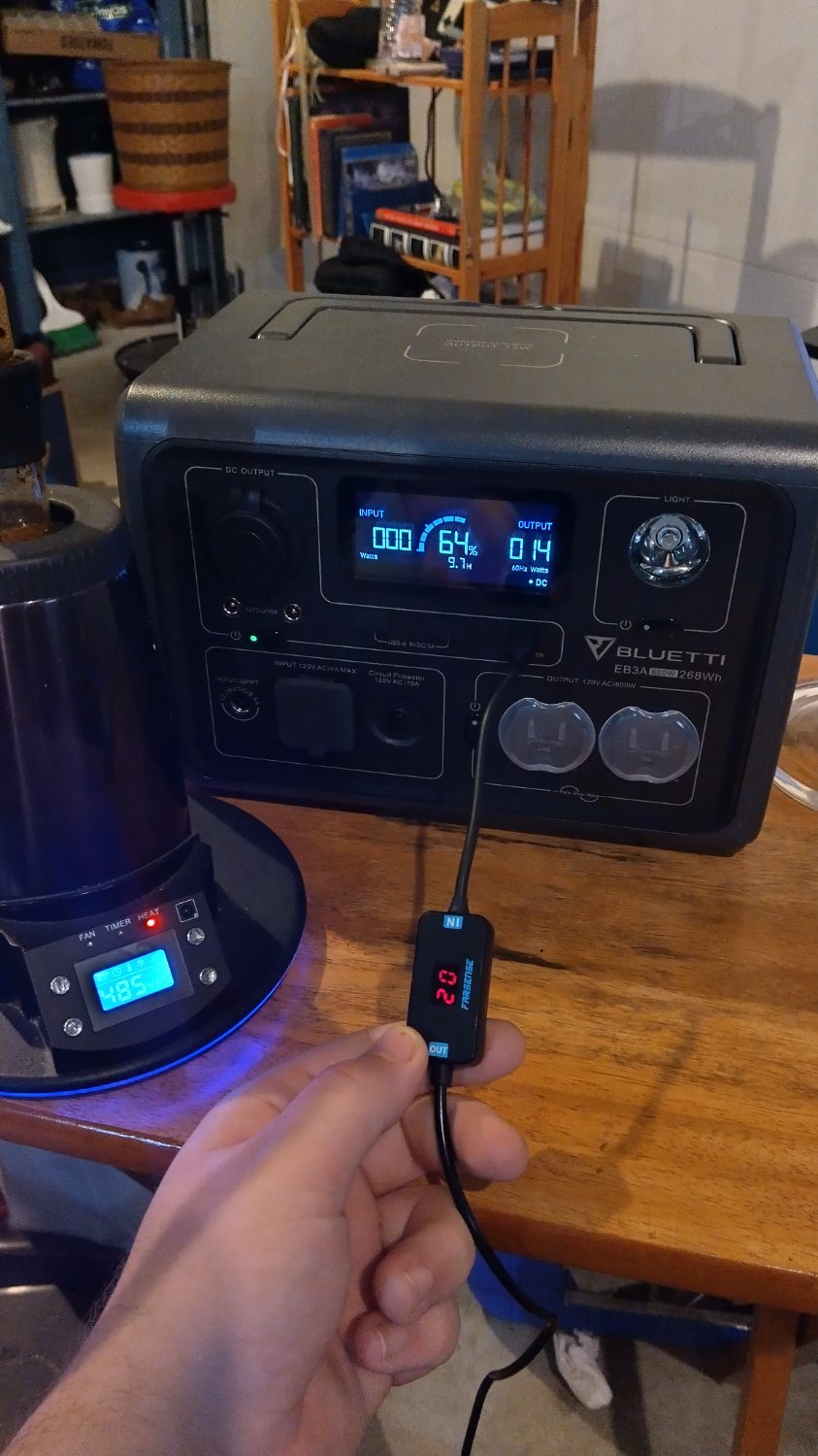

Do you know how magical that is? How much trouble that saves when it comes to mcguyvering a DC appliance that only came with AC cable to supply proper power directly? All I need is a 10$ usbc-pd to barrel plug cable that manually selects the voltage needed and some barrel plug adapter bits to fit into the appliance. Energy efficent and simple wiring. All the dynamic controller stuff is abstracted away in a safe way. Powerful enough to deliver 100 watts of power, and its going to be more powerful over time.
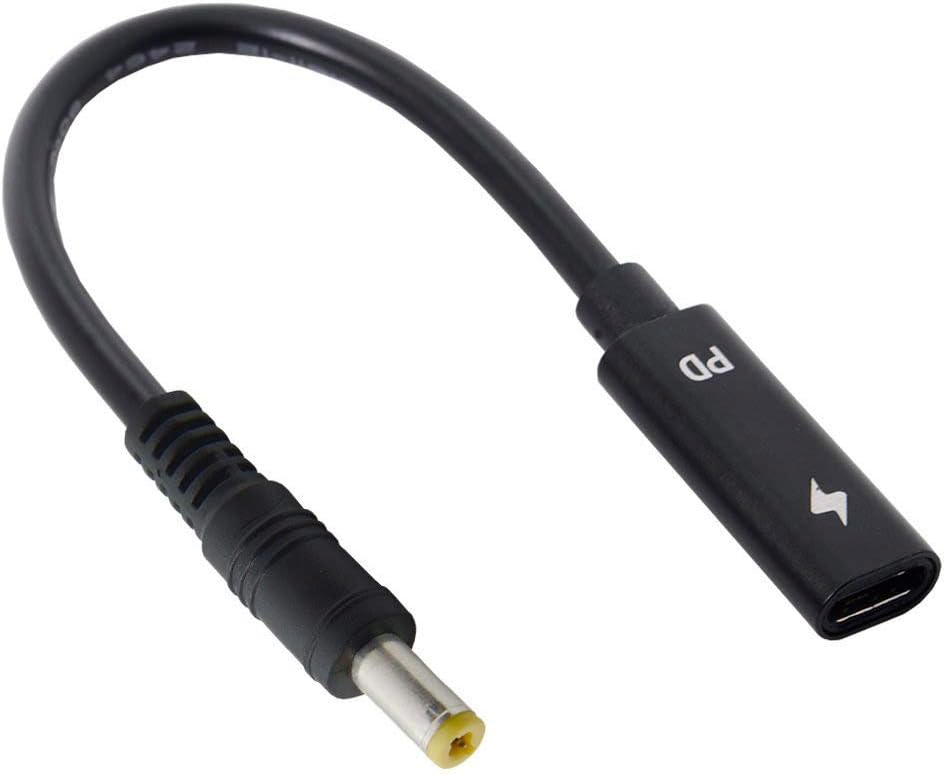
now someone needs to make USB-C jack to barrel plug “tips” with the PD chip built in so I can substitute USB-C for wall wart transformers.
Hey aubeynarf think you are talking about something like this.
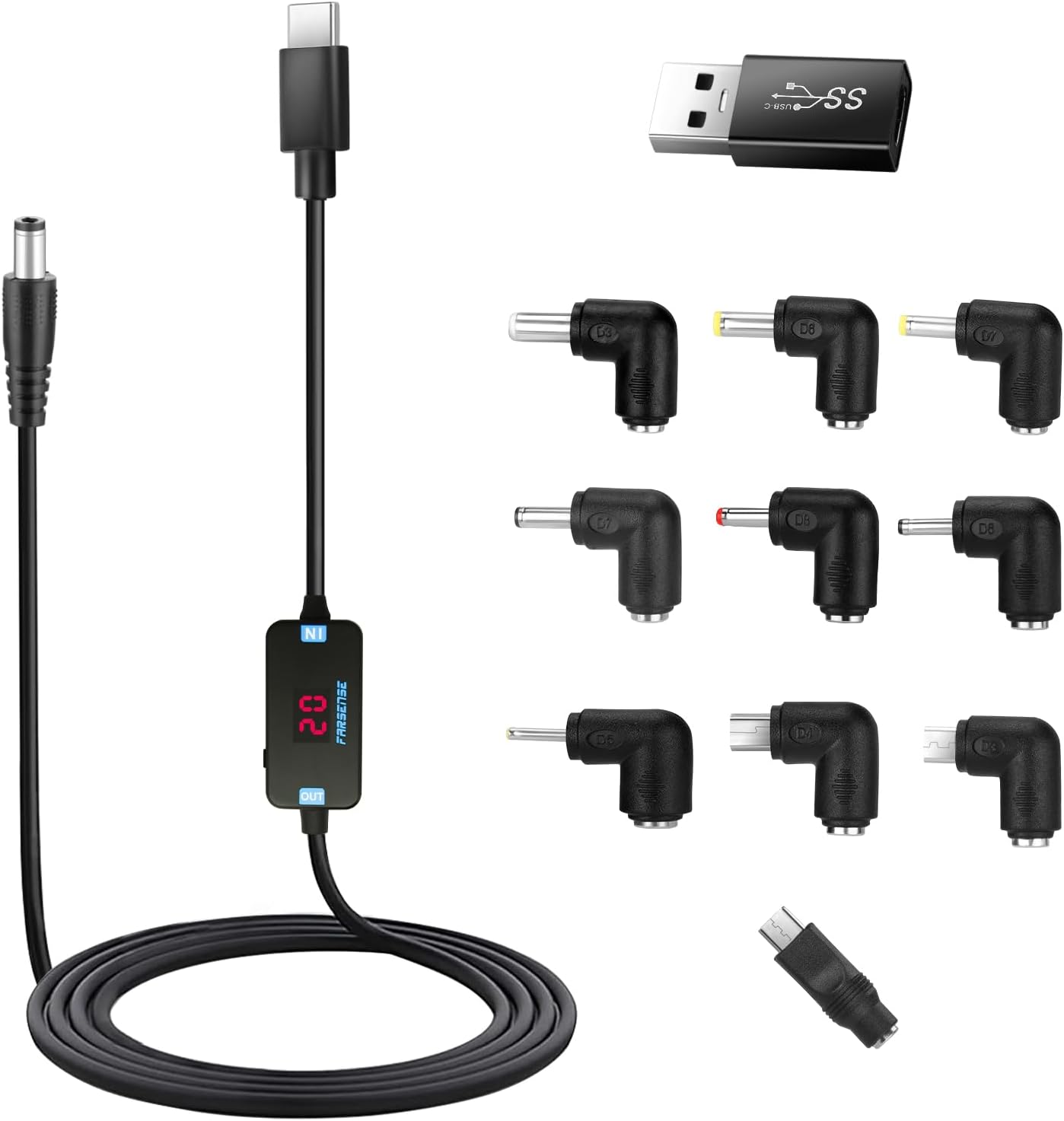

Its a special usbc-pd to 5.5x2.5 barrel jack with manually selectable voltage. You just plug it into a pd charger and select the voltage of the device. The rest is finding a barrel plug to barrel plug adapter that plugs into your device. Hope this helps.

I want that whole arrangement to be in a tip with a USB-C receptacle and a fixed voltage and barrel size so it’s barely bigger than my thumbnail and can be used with standard usb-c cables.
So I can get a “9V-5.5x2.5-Pos” to convert my casio keyboard to usbc, without all that other stuff hanging off and extra, unnecessary pieces
But yeah that’s cool
If your device happens to be 18-20v you can get a usbc-pd laptop connector with a dc barrel jack output. It has the USBC-PD chip built into it to tell the charger to output 20v and you can probably hunt down barrel adapter bits. Your regular 65-100w rated usbc cord plugs in like anything else.

The other voltages are tough theres not really a consumer market for 15v or 9v specific usbcPD to barrel things.
I appreciate that you’re really thorough, both with that explaination as well as the implementation in the first place.
I guess I’ve never give it much thought. I mean, I’m familiar with electricity, but I’m paying dirt cheap for it.
One more question: How do you do your lighting? Most light fixtures I know are using e27 bulbs, which are AC powered. I know the LED panels requires driver circuits between them and the main, theoretically they probably could live off your DC straight-up, but they’re generally a pain to work with.
Thanks. Lighting has been an ongoing puzzle I’m figuring out. I originally went with rechargeable Luci light it was really nice warm bright lighting but expensive and failed within a season. Currently I’m using a cheap 5v plastic led light bulb that plugs into regular usba slot. Its enough to see what you are doing comfortably. But really the average person whos used to house bulbs including me wants the luxury of bright lighting. For now I’ve been firing up the AC inverter to run a nice lamp. However I have been considering making my own 12v light fixture with 12v e26 bulbs that plugs into either car cig plug or usbc-pd.
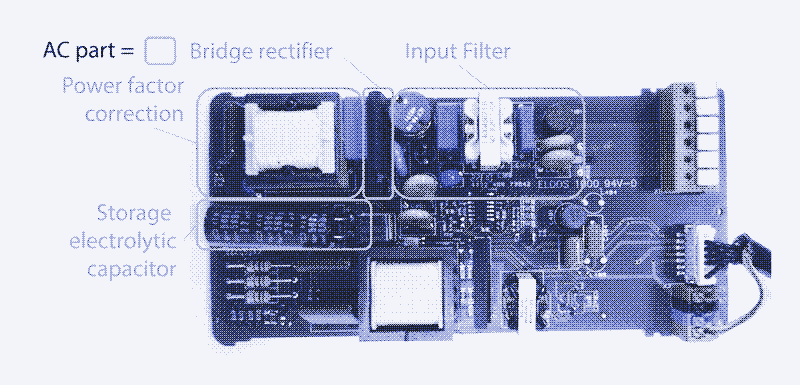
In this picture is marked all the parts of an LED circuit that convert AC Into DC. It takes up about 40% of the board. Its much easier to power LEDs directly.
-
Really hasn’t been much of one. I still own devices that charge from MicroUSB, a lot of peripherals are still USB-A, there hasn’t been any significant movement by the industry overall to move everything to C, so mostly it means I just need to carry more cables.
A big one. No more brittle micro usb, which would eventually become loose and start falling out when charging. Being able to charge my laptop using my phone charger is also good.
Not at all, the “biggest change” was with fast charging, but Li-ion batteries hate being at 0 or 100% all the time and fast charging makes it too easy to ovrtcharge to 100, and I’ve only got 1 device that can do “fast charging speeds” (over 9w). Most of my electronics are a mix of type c and micro to type a. A c - c cable is like with my fast charger is overkill for my application and is inconvenient when the vast majority of charging bricks and plugs have type a charging.
It’s been more of a pain in the arse than initially expected.
Most motherboards (for example) only have 2-4 USB-C ports, meaning that I still need to employ A-C and C-C cables for peripherals etc.
My main gripe is that the standard just tries to do too many things without clear delineation/markings:
-
Is it a USB 2.0 (480Mbit), 5Gbit, 10Gbit or 20Gbit cable? Can’t really tell from the plug alone.
-
More importantly, for charging devices: How the heck do I determine maximum wattage I can run?
For all its faults, at least the blue colour of a USB-3.0 plug (or additional connectors for B/Micro) made it easy to differentiate !
Now I’m eyeing up a USB Cable tester just to validate and catalogue my growing collection! 🤦🏻♂️
USB Cable tester
Great idea, and then:

I was actually thinking coloured O rings to define specs, but that still means I’d need to have a colours guide somewhere too…
…yours might be a more practical solution. 🤔
You could fit some key numbers and letters on those O rings, I like it!
It’s even more annoying that there are different possible pinouts in the port itself without clear labling. So always use the one cable that came with the peripheral, or you have a chance to fry it
Just recently I had a tech store guy gently but repeatedly insist to me that a certain USB cable was a USB 3 cable because it was type C on both ends. I didn’t wanna argue with him, but the box clearly said “480 Mbit”, so it was just a type C charging cable.
Of course the box designers were hoping you’d make that mistake so they didn’t write USB 2 on there, just the speed. And most boxes won’t even have that, you’ll just have to buy it and see.
But I mean if someone who spent their whole life fixing computers can get something that basic wrong, then it’s really a hopeless situation for anyone who isn’t techy.
And of course once it’s out of the box it’s anyone’s guess what it is. It’s a real mess for sure.
I wonder about this too. Can I plug my laptop’s USB-C charger into my phone? Or is that a big nono
Yes, you can. The charger and the device communicate between one another what they can support, and pick the highest one they both agree on.
E.G. my laptop charger can charge at full speed (100W) for my MacBook, but only at 20W for my iPhone.
That bit is pretty straightforward and transparent to end users (there are a few rare conditions where devices might not agree on the fastest, and have to fall back to a slower one); the issue is more with cables not having sufficient gauge wire, or missing connections that prevent the charger and device from communicating their full functionality.
Yes.
I charge by Bluetooth headphones ‘pod’ with my Steam Deck charger and it seems to be ok.
The deck charger uses USB PD. It will charge anything that supports the standard as fast as possible (up to its rated 65W) and use normal 5v USB for everything else.
For the power matter, you don’t. The device being charged, the charger, and cable does.
If you mean what is the maximum wattage that will actually be used, that should be the maximum possible between the charger, cable, and device. So look at their specs. Whichever has the lowest maximum, is what the others will match.
USB PD defines a protocol for the device and charger to determine max safe power. If the cable is replacable (not attached to the charger), it must be rated for PD and be able to tell the charger it can handle more than just the usual 5 volts at 2 amps.
USB PD chargers only output the maximum safe amount of power. That’s why I can use my 65W steamdeck charger to charge my phone if I want to. It just outputs normal USB charger power if the device on the other end can’t verify it can handle more.
It’s also why my SteamDeck charger is what I use to fast charge my phone, because it can actually talk to it using the USB PD protocol to request the voltage and amps it needs to fast charge.
To clarify; I have a 100W Ugreen Nexode 4 Port USB Charger that I use to charge my laptop (~60W), Steam Deck (~40W), iPhone (~20W) and AirPods (~5?W).
The problem is if my original product cable has gone walkabout temporarily and I need to use a random one to stand in - there is no clear way of telling if I’m accidentally using a 5W-max cheap cable to try and keep my laptop charged while working.
Obviously there are some context clues depending on cable thickness etc., but with how common cosmetic braiding is becoming a thing - even that’s getting harder to rely on.
Some kind of cable labeling would be nice.
-
With a laptop and phone which both can use it my backpack while travelling is so much lighter and less bulky. For me it absolutely was a game changer, I just don’t like that I need to carry a USB a to C adapter for all the legacy USB A ports.
Works great, rarely have issues with the port breaking unlike prior small usb standards, it’s nice how ubiquitous it is so I have way less random cable connectors around.
Not at all a game changer, for me.
I mean, it’s just another and one more type of cable. Sure, in theory it’s simpler than many various cables and it’s even less stupid than the previous USB types, but it’s still a mess.
At least, for non-geek me, those cables are a mess as I need to be able to distinguish between the exact same cable to find which one is USB-C or Thunderbolt, between the various versions of USB-C itself, and then between USB-C that comes with or without power delivery, and with what power limitation? And then, despite USB-C supposedly being a standard there are still too many cables that just won’t work with certain devices because reasons.
Add to that the many USB-C docks (and dongles) that work… more or less reliably and more or less as marketed (even more so under Linux, but those issues exist under Mac and under Windows as well).
Older cables and ports were cumbersome, and thick and whatever but, as far as I’m concerned, for the most part they just worked like they were supposed to. And I never had an issue knowing which cable to plug into which port as they all looked, you know, different.
Nowadays, I have to label each one of my USB-C cable with some masking tape so I can identify it in a glimpse without wasting my time trying them all one by one.
Edit: some clarifications.
I was pretty fucking disappointed how flimsy the jacks are.
I’ve had 3 phones and a laptop I had to replace because the USB-C jack started to wiggle and wouldn’t connect anymore.For charging, it’s fine, I have equipment to do some mid level testing of how much power a USB cable can transmit, I can also verify if a charger supports quick charge and other charging protocols.
For data transfer, it’s frustrating, you gotta find the cables that are not just USB2 with a USB-C connector.
Then you have thunderbolt, which is even more expensive…
I don’t think I’ve had a single USB-C cable/connector/socket fail yet. Which can’t be said of Micro-USB.
But other than that, meh.
Game changer? Literally not at all. It’s a bit better.













